Analysis of IPS TFT LCD
IPS TFT LCD is an optimized LCD technology using an in-plane switching liquid crystal array (IPS) coupled with a thin-film transistor driver. Its core advantages include ultra-wide viewing angles, precise color accuracy, and touch-resistant, ripple-free operation, effectively addressing the viewing angle and color issues of traditional LCDs. However, it also suffers from limitations such as high power consumption, low contrast, and high cost. Its application scenarios span consumer electronics, professional equipment, industrial control, and other fields, making it the mainstream choice for mid- to high-end display products, particularly those requiring a superior viewing experience and color accuracy.

- Model: TFT-H013A6QQIGC7N10-V1
- Type:1.28 inch IPS TFT LCD Display
- Display pixels: 240×240 px
- Overall dimensions (Mm): 35.6×38.1×1.6
- Effective size (Mm): 32.4×32.4
- Brightness: 750cd/m2
- Pin: FPC-10PIN
- Working temperature: -20~70℃
- Power supply voltage: 2.8V
- Driver chip: GC9A01

- Model: TFT-H050A12FWIST4C40
- Type:5 inch IPS TFT LCD Display
- Show contents:480×854 px
- Outline size(mm) :72×122.25×4.15
- Effective size(mm):61.63×109.65
- Backlight type or brightness:400cd/m2
- Connection PIN Number:40pin
- Working temperature:-20~70℃
- Power supply voltage:3.3V
- Driver chip model:ST7701S
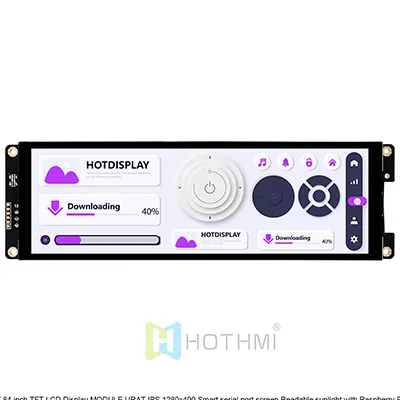

- Model: TFT-H068A05ZAINV5C50
- Product type: TFT strip
- Display content: 480×1280
- Overall dimensions (mm): 73.50×195.39×6.5
- AA size (mm): 60.192×160.512
- Brightness: 500cd/m2
- Number of PINs: FPC-40PIN
- Touch: capacitive touch screen
- Interface mode: LVDS
- Supply voltage: 3.3V
- Driver chip: NV3052
- Touch chip: GT911
What is IPS TFT LCD
IPS TFT LCD (In-Plane Switching Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display), a leading display technology widely used in smartphones, computers, and televisions, has become the preferred choice for mid-to-high-end displays. By optimizing liquid crystal molecular alignment, this technology effectively addresses key challenges in viewing angles and color reproduction, making it a go-to solution for premium display applications.
IPS TFT LCD technology composition
Technical modules | Key role | Popular explanation |
TFT | Signal control layer | It is equivalent to the “pixel switch”, which provides independent current signal for each LCD pixel to accurately control the brightness of pixels, avoid the problem of “shadow” in traditional LCD, and achieve high resolution and fast response. |
LCD | Image generation layer | It works by using the “light deflection characteristics” of liquid crystal molecules: liquid crystal molecules themselves do not emit light, so they rely on backlight layer (such as LED). By changing the arrangement Angle of liquid crystal molecules, the amount of light passing through them can be adjusted to present different brightness and color. |
IPS | LCD arrangement optimization technology | By changing the “vertical arrangement” of liquid crystal molecules in traditional LCD, the molecules are rotated in the same plane, which fundamentally solves the problems of viewing deviation and color distortion. |
How IPS TFT LCD works
The working process of IPS TFT LCD can be divided into four core steps: “signal control → liquid crystal rotation → light adjustment → color synthesis”, as follows:
Signal input and TFT drive
When a device (such as a mobile phone or computer) outputs an image signal, the signal is transmitted to the TFT layer of the display. The TFT acts as a “pixel-level controller,” applying specific voltages to the two transparent electrodes of each pixel (located on both sides of the liquid crystal layer). The voltage magnitude determines the rotation angle of the subsequent liquid crystal molecules.
Liquid crystal molecular plane rotation
The core of IPS technology lies in the alignment of liquid crystal molecules. When not powered, these molecules remain parallel to the screen plane, with light from the backlight layer filtered by polarizers preventing penetration (resulting in a black screen). Upon activation, under the influence of electrode voltage, the liquid crystal molecules rotate at specific angles within the same plane (unlike the vertical flipping characteristic of traditional LCDs), with rotation angles determined by voltage intensity (higher voltage leads to greater rotation).
Backlight penetration and brightness control
The backlight layer at the bottom of the display (typically an LED array) continuously emits white light. This light first passes through a lower polarizer (which filters out non-specific directional light) before entering the liquid crystal layer. Since the liquid crystal molecules have rotated, they “guide” a specific amount of light through the upper polarizer ——. The greater the rotation angle, the more light is transmitted, resulting in higher pixel brightness.
Color filter and image synthesis
A color filter is positioned above the polarizer, with each pixel containing three sub-pixels (red, green, blue) corresponding to specific filter regions. When white light passes through these filters, it breaks down into red, green, and blue primary colors. By adjusting the brightness ratios of these sub-pixels, the TFT displays can mix these colors to create any desired hue (e.g., red + green = yellow). All pixels work together to form a complete color image.
Core advantages of IPS TFT LCD
Compared with traditional TN-LCD (twisted nematic) and VA-LCD (vertical alignment), IPS TFT LCD has advantages in three core dimensions: viewing Angle, color and picture quality.
- Ultra wide Angle, no viewing bias
- Color accuracy, true to life
- Pressing the waterless wave, the touch experience is better
- Fast response speed, smooth dynamic picture
Comparison of TN/VA/IPS
Comparative projects | TN-LCD (twisted nematic) | VA-LCD (vertical alignment) | IPS-LCD (planar conversion type) |
price | lowest | secondary | Best (compared with the same parameters) |
angle of view | difference | preferably | Optimal (full view 178°, no attenuation of color/brightness at any Angle) |
Color accuracy | difference | preferably | Optimal (color gamut coverage of 72%-99% sRGB, high color consistency, no local color bias) |
Black level | difference | optimal | Medium (slight light leakage, dark gray black field) |
contrast ratio | low | highest | Medium (static contrast ratio 1000:1-1500:1) |
reaction time | fastest | secondary | Medium (native response time 3ms-5ms) |
refresh rate | tall | secondary | Medium (mainstream support 60Hz-165Hz) |
power dissipation | lowest | secondary | The highest ( the backlight maintains high brightness) |
Pressure characteristics | difference | secondary | Optimum (no water ripple, stable structure) |
IPS TFT LCD's disadvantages
Category of shortcoming | Technical reasons |
High power consumption, high battery life pressure | 1. The rotation of the liquid crystal plane requires a higher voltage (20%-30% higher than TN-LCD); 2. The wide viewing Angle requires the backlight layer to maintain high brightness. |
The contrast is relatively low | The LCD can not completely block the backlight, and the light leakage in the dark area leads to low static contrast. |
The cost is high and the price is high | 1. High requirements for liquid crystal arrangement and process precision; 2. The production yield is lower than TN-LCD/VA-LCD. |
Light leakage is common | 1. The backlight layer does not emit light evenly; 2. The sealing process of the frame is not accurate enough. |
HOTHMI is a company specializing in IPS TFT LCD
HOTHMI specializes in the R&D, production, and sales of IPS TFT LCD products, leveraging the core strengths of IPS technology to ensure a product qualification rate exceeding 99.5%. The company also offers flexible customization services (screen size, resolution, interface, touch functionality) and 24/7 technical support, positioning itself as a trusted partner for global clients seeking high-performance IPS TFT LCD solutions.